In an age of convenience and knowledge at our finger tips, we expect so much from technology at a faster rate. Thankfully, technology has not yet disappointed us with innovations. Computer companies are competing on the most versatile and compact laptop, car companies are competing on who has the best electric car, and cell phones are now mini-computers. The only innovation missing is hover boards (i.e. Back to the Future).
What are LED lights?
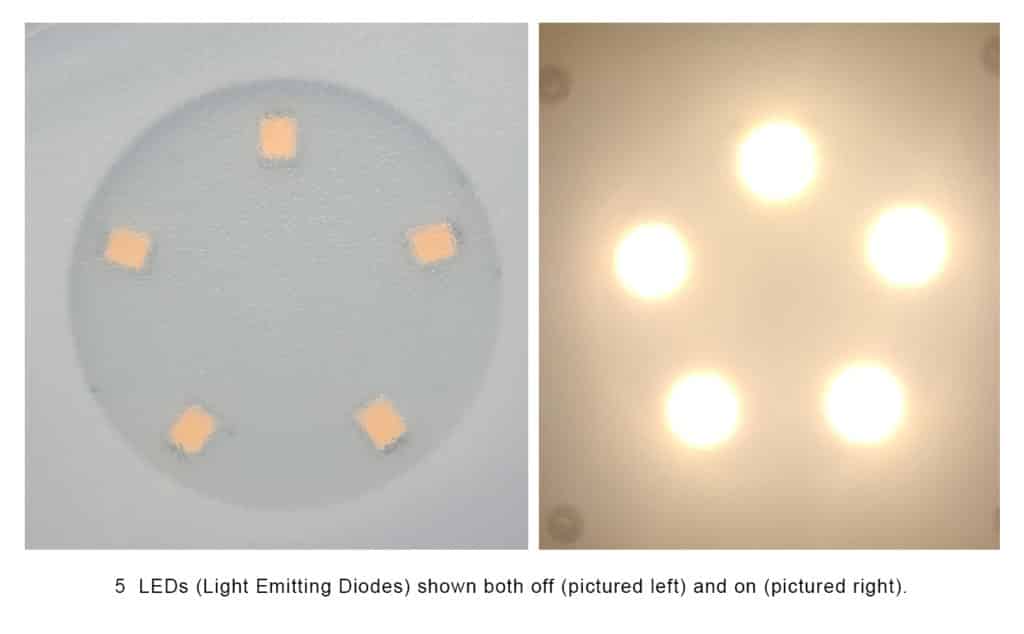
LED is an acronym for Light-Emitting Diode. A LED is a small device that acts as a semiconductor emitting light when an electric current passes through. Many times, a LED lighting fixture or bulb is made up of multiple LEDs on a singular board to produce the desired amount of light for the product.
Household Use: LED vs. CFL vs. Incandescent
With the introduction of the Energy Independence & Security Act of 2007, lightbulbs of 100W or greater disappeared from shelves. In 2022 new rules were set into motion by the U.S. Department of Energy to ban the sale of bulbs that produce less than 45 lumens per Watt. Though changes like this cause discomfort and short term inconvenience, it’s a good thing. As much as we love initial low prices, whether we like it or not, environmental factors will become more prominent over time in the lighting and energy industry. These factors will create new standards for energy-efficiency and sustainability.
What is the difference between the light bulbs you are able to buy off the shelves?
LED
- HEAT: 3.4 btu’s/hour*
- 40x longer life than incandescent
- Significantly lower wattage
- Better for the environment
- Reduced electric bill
- Longer Life
- Higher upfront cost
- Durable
CFL
- HEAT: 30 btu’s/hour*
- Contains mercury and needs proper disposal
- Lower wattage used than incandescent
- 6x long life than incandescent
- Not environmentally friendly
- Sensitive to extreme temperatures and humidity
- Takes time to warm up to reach full lumen output
- Not durable
- Possible to catch fire, smoke, or emit odor
Incandescent
- HEAT: 85 btu’s/hour*
- Not durable
- Significant carbon dioxide emissions
- Significant energy consumption
- Initial cheap cost, higher long term costs
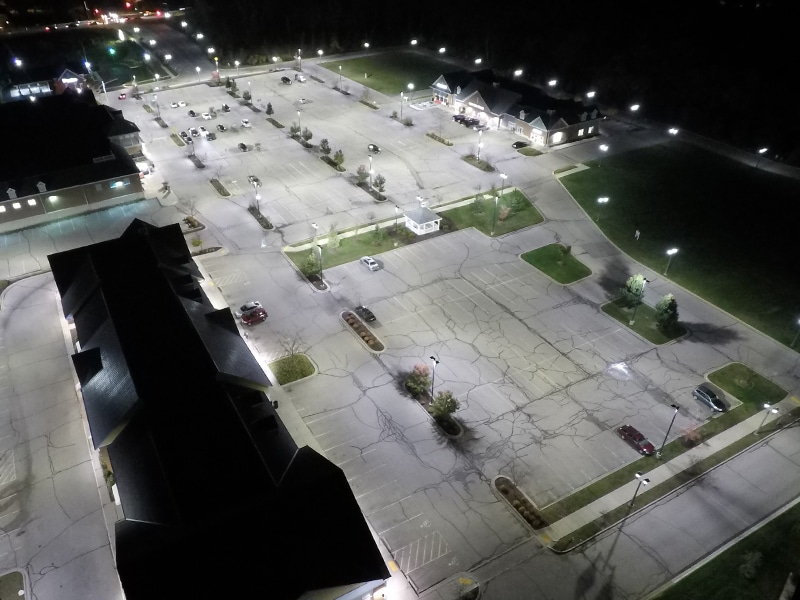
Commercial Use: LED vs. Metal Halide
For the sake of LED, we will only be looking at Metal Halide bulbs for comparison.
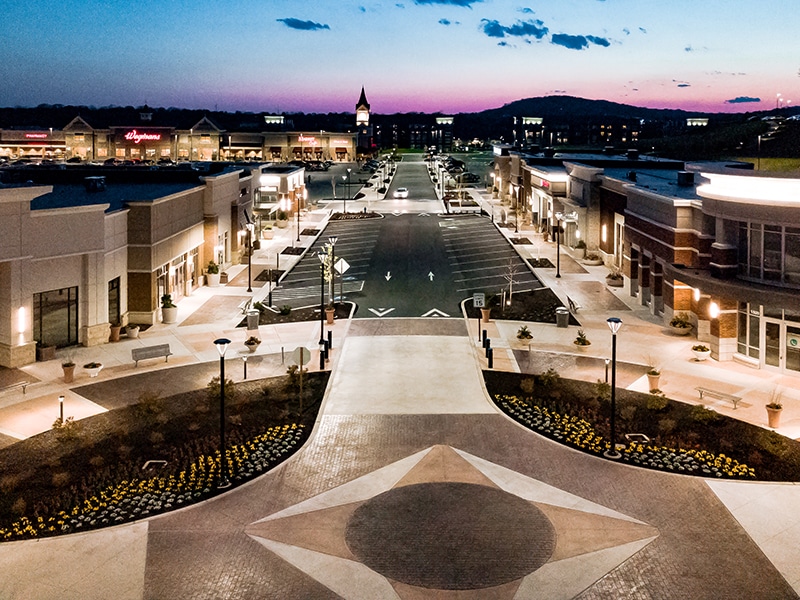
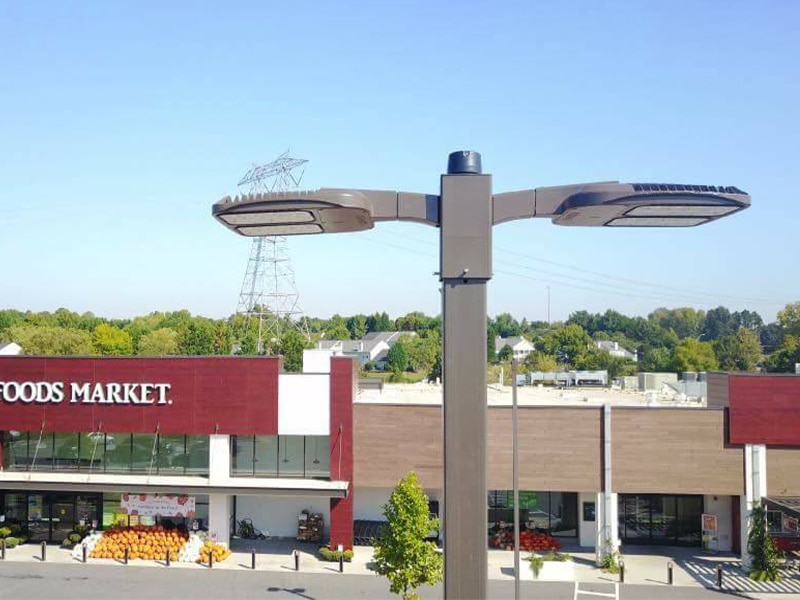
Commercial Use refers to lighting fixtures in commercial applications such as parking lots, exterior building façade, warehouses, shopping centers, industrial structures, etc.
Metal Halide (MH) produces light by a mixture of gases inside the bulb (Yes, they contain traces of mercury as well). MH works under extreme pressure and at very high temperatures. Just like a CFL bulb, MH takes some time to warm up to reach its’ maximum lumen output. MH can also be unstable if you do not maintain proper maintenance. Group re-lamping is necessary to help fight against the possibility of the bulb exploding.
LED commercial fixtures have a higher luminaire efficiency, lower optical loses, generate significantly less heat, and are more uniform in lighting output. Most LED fixtures come with a 5 – 10 year warranty and are estimated to last anywhere from 50,000 HRS to 100,000 HRS (MH averages about 20,000 HR).
Energy.gov has some great information on Area Lighting here.
Aren’t LEDs bad for your health?
No, LEDs are not bad for your health. This is a common myth about LEDs!
You remember when your mom used to tell you that if you eat too much pizza, you’ll turn into a piece of pizza? The common idiom, too much of a good thing is never a good thing, comes into play. That of course goes with many everyday activities and products we use as well as LED lighting. Too much of a certain type of light can disrupt your sleeping patterns if you’re not careful with your habits. Since their introduction into the lighting industry, LED technology has grown a lot. It’s common to see different temperatures of LED bulbs available – usually a soft white (warmer hue) and a white cooler light. The temperature of lighting should be considered when you utilize light to improve your circadian clock. Learn more about the relationship between your health, lighting, and circadian rhythm at our blog here!
Since LEDs use less wattage, won’t they be dimmer?
Nope!
That’s one of the greatest advantages of LED lights. LEDs can hold the same amount of lumens as another bulb but use significantly less energy. As technology continues to improve, LEDs will only become sustainable at better prices.
What is the difference between lumens and watts?
Lumens is the amount of light that is emitted by a lighting source. This differs from watts by a complete different measurement. Watts is the amount of energy that is used when a device is turned on. Traditionally, the more lumens a light had, the greater the energy usage (or wattage). Now, with the introduction of LED lights, you can fulfill more lumens at an exponentially lower wattage.
Why are LEDs so much more expensive?
In the past decade, LEDs have already decreased in consumer price exponentially. This is one of the only cons of LED lighting: Price. Though you are spending more upfront with LED, you are investing in a product that has on average 40x longer life ultimately saving money on your energy bill.
Want to learn more about how to make your property greener and more energy efficient with lighting? Email your favorite WLS lighting expert today at [email protected] – Call us at 800-633-8711